Retrieving Advanced Security Information
One feature integrated into GENESIS64™ security and GraphWorx™64 is the ability to query the level of access the logged-in user has on a Data Point, Alarm, File, and so forth. This feature also lets you secure GraphWorX64 further and incorporate these values into expressions or dynamics.
This topic describes several advanced features of GENESIS64 security, including showing a user logged in through a GraphWorX64 Local Simulation variable, retrieving and displaying the user's level of access on a Data Point, Alarm, and File, and showing you how to verify the custom string against the logged in user.
Setting up Security
The following steps creates one user that gets used in other examples within this topic.
- From the Security >Users, right-click Add User.
- Create a new user called TestUser.
- For the steps, it will be presumed the “Allow these operations” for all tabs has an * in it. If it does not, please do so now.
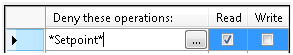
- On the Points tab enter *Setpoint* in the “Deny these operations” section and remove the check mark from the Write column as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 - Security Points Configuration
-
On the Alarms tab enter *Pump* in the “Deny acknowledgement of these alarms” section.
-
On the Files tab enter *Supervisor* in the “Deny these” section and remove the check mark from the Create and Modify columns as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 - Security Files configuration

-
On the Custom tab enter customString in the “Deny these operations” section.
-
Click Apply to save your changes.
NOTE: The * (asterisk) wildcard is used to represent zero or more characters. For more information, refer to Wildcards and Performance Optimization.
For more information on setting up, refer to the GENESIS64 Security - Quick Start topic.
Displaying the Current Logged-In User
There is a local simulation variable available in GraphWorX64 that retrieves the current logged-in user.
- Open a GraphWorX64 display.
- Add a Process Point to the display.
- For the Datasource enter localsim::currentUser
-
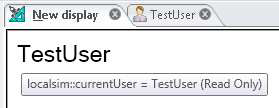
Enter runtime and the Process Point should show something similar to Figure 3.
Figure 3 - localsim:currentUser in a PPT
You can then retrieve the logged-in User from a script by getting the value of this Process Point. Please refer to the Scripting - Quick Start topic for more information on scripting.
Retrieving Read, Write, and Modify Permissions
Once you have security configured, you can view what level of access the current user has by using a special syntax available to GENESIS64. The syntax is:
?Category:comparison string
The Category can be any of the following
- ApplicationAction
- DataPoint
- Alarm
- File
- Station
- CriticalPoint
- CriticalAlarm
- Report
- Transaction
- Custom
The “comparison string” is basically any text that follows such as an OPC tag or a simple string. For example the following are valid ways to retrieve the level of security for an alarm called “LowPressure” and an OPC tag from the ICONICS Simulator OPC Server:
?Alarm:LowPressure
?DataPoint:@ICONICS.Simulator.1\SimulatePLC.OUTPUTS.FLOAT1.Value
With the proper syntax in place, the following truth table shows the possible values this special security syntax can return. The resulting values are the decimal representation of the binary bits being true.
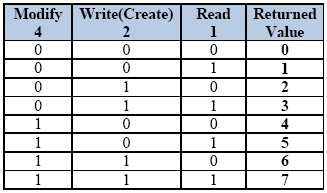
NOTE: Depending on the category you are trying to access (DataPoint, Alarm, File, etc.) the Modify and Write/Create may not apply.
Let's now bring the above topics together with an example we started to configure in the previous section.
- Open a GraphWorX64 Display.
- Add a new Process Point using each of the following Datasources:
?DataPoint:localsim:TankSetPointLow
?Alarm:PumpStatus
?File:MaintenenceSupervisorControl
-
Put the display in runtime and you should see values similar to the ones in Figure 4.
Figure 4 - Results in GraphWorX64 Runtime
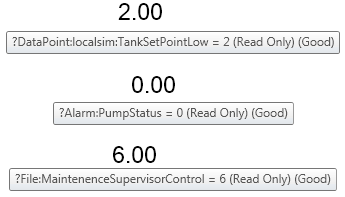
Keep in mind that the Deny permissions take precedence over the Allow when manually calculating these values. If you have been following this example, then there should be an * in the allow fields of each tab to allow everything by default. Feel free to experiment further with different combinations of Read, Write, and Modify permissions.
Displaying Information About the Currently Logged-In User
ICONICS security exposes some information about the currently logged-in user through various data points. Using GraphWorX64, the following data sources can be visually displayed.
|
Data Source |
Description |
|---|---|
|
?Current:UserName |
Displays the name of the currently logged-in user. |
|
?Current:CustomID |
Displays the custom identifier of the currently logged-in user or for one of the group(s) that the user is a member of.
|
|
?Current:LanguageCultureName |
Displays the default language settings of the currently logged-in user or for one of the group(s) that the user is a member of.
|
|
?Current:Groups |
Displays a comma-separated list of groups that the current user is a member of. |
|
?Current:PasswordExpiration |
Displays the date/time in UTC when the password of the current user expires.
|
Checking Custom String from a GraphWorX64 Script
If you are familiar with GraphWorX64 scripting you should be able to easily see the currently logged-in user by trying the steps below. Refer to the GraphWorX64 Scripting topics for help. For example, refer to Scripting - Quick Start.
- Open a GraphWorX64 display.
- Add a button that will use the Run Script command and give the script a name.
-
In the Script Editor, use the ThisWindow.IsCustomSecurityAllowed(“customString”) function. For example:
var result : Boolean = ThisWindow.IsCustomSecurityAllowed("customString");
MessageBox.Show(result);
- This should display a message box with a value of “false.”
See also:
 If a specific value is configured at the user level, then this will be the value of the data point. If the current user has no specific value configured, then the value configured on one of its groups is used. If multiple groups have a value configured, then the value will be randomly one of those.
If a specific value is configured at the user level, then this will be the value of the data point. If the current user has no specific value configured, then the value configured on one of its groups is used. If multiple groups have a value configured, then the value will be randomly one of those.