SPC Tag
To Create an SPC Tag:
-
Start the Workbench, then expand your project. Next, expand the Historical Data node to show the Hyper Historian node. Expand the Hyper Historian node to show the Data Collections node.
-
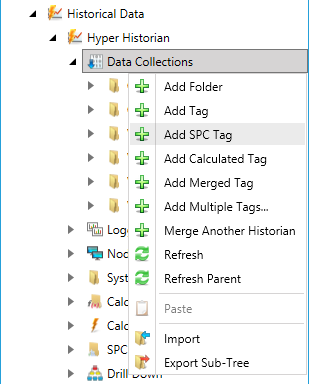
Right-click the Data Collection node in the navigation tree, or any of its sub-nodes, and select Add SPC Tag, as shown in the figure below.
Add SPC Tag from the Project Explorer
-OR-
Select the Data Collections node in the Project Explorer, or any of its sub-nodes, then click on the Add SPC Tag button, shown below, in the Edit section of the Home ribbon in the Workbench.
Add SPC Tag Button
-
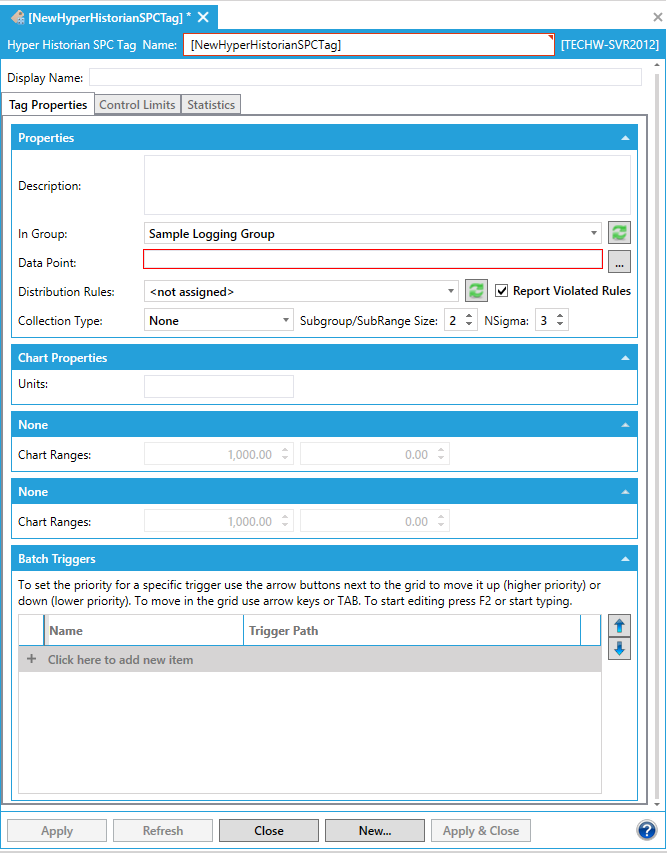
This opens the Hyper Historian SPC Tag properties window, shown below, beneath the Project Details section in the Workbench. Enter a name in the Hyper Historian SPC Tag Name text entry field.
Hyper Historian SPC Tag Properties
-
The SPC Tag Configuration Dialog allows you to configure the settings associated with a new SPC tag or edit the settings associated with an existing SPC tag. The dialog is divided into the following three sections:
Tag Properties Tab
The Tag Properties tab allows you to set how an SPC tag is organized within Hyper Historian, the source for the raw data that the SPC tag summarizes, the distribution rules that the tag follows, and the types and triggers for grouping sample values that the SPC tag collects.
- In the Properties section of the tab, enter a Description (optional) for the tag to explain its purpose.
- For the In Groupfield, select the logging group with which this tag is associated.
|
|
Note: If you have recently created a logging group, you may need to select the Refreshbutton to have it appear in the list of groups underIn Group. |
-
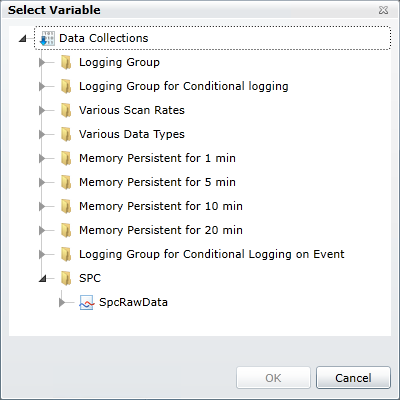
Click the ellipsis button [...] next to the Data Point field to browse for the data source that produces the raw data for this SPC tag. The
 Data Browser window appears. It is convenient to use a raw data tag similar to the one you created in the same folder as this SPC tag.
Data Browser window appears. It is convenient to use a raw data tag similar to the one you created in the same folder as this SPC tag.
|
|
Note: If you have recently created a raw data tag, you may need to select the Refreshbutton in theSelect Variabledialog to be able to select this data tag. |
-
Select a set of Distribution Rules for this SPC tag using the provided drop-down list. Each set of rules defines a set of criteria for determining whether recent SPC tag values reflect an out-of-control process. See the SPC Distribution Rule Sets topic for information on editing existing distribution rule sets or creating new rule sets.
-
Optionally select the Collection Type, or the values used to summarize a subgroup of SPC tag samples, using the provided drop-down list. You can select subgroup summary values of mean/range (XBarR), mean/standard deviation (XBarS), median/range (MedianR), or individual data points/moving range (XMR).
-
Choose a Subgroup/SubRange Size by entering a value into the provided textbox or pressing the up and down arrows to select a value. This field defines the number of samples in each subgroup for the SPC tag. By default, this value is 2, indicating that each subgroup contains 2 samples.
-
In the Chart Properties section of the tab, enter the Units associated with the summary values into the provided textbox.
-
In the next two sections of the tab (labeled according to the collection type you have selected in step 5), select a Hi Limit and a Lo Limit for each summary value that appears on the chart summarizing this SPC tag.
|
|
Note:If you have left theCollection Typevalue blank, theHi LimitandLo Limitsettings will remain disabled. |
-
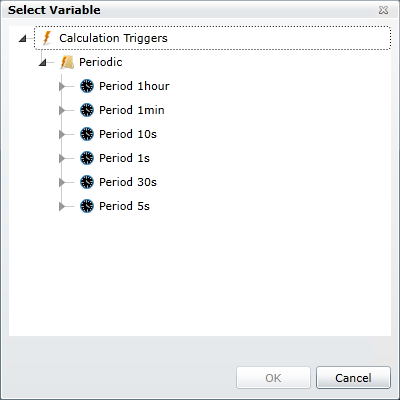
In the Batch Triggers section of the tab, you can select one or more calculation triggers that determine when the SPC tag should stop summarizing subgroups within one groups and begin collecting subgroups in a new group. Press the square button on the right-hand edge of the Trigger Path column to open the
 Select Calculation Trigger dialog.
Select Calculation Trigger dialog.
|
|
Note: If you have recently created a calculated trigger, you may need to select the Refreshbutton in theSelect Variabledialog to be able to select this trigger. |
-
Select the text in the Name column to change the default name given to a batch trigger.
-
If you have added more than one trigger, you can press the up and down arrow buttons to increase or decrease a trigger's priority. Triggers that appear near the top of the list have higher priority.
-
Continue configuring this SPC tag using the settings on the Control limits tab or the Statistics tab.
Control Limits Tab
-
The Control Limits tab allows you to define the reasonable limits of variation in the values that the SPC tag generates and calculates. Values that fall outside of the limits you define here represent an out-of-control process. Enable the Constant Limits radio button if you wish to define constant values for limits, and enable another radio button if you wish to calculate limits based on the SPC tag values.
|
|
Note: If you have left the Collection Typevalue blank, the settings on this tab remain disabled. |
-
If you have enabled a radio button other than "Constant Limits" within the "Control Limits" tab:
-
For the Calculate Everyfield, enter the number of samples that the SPC tag should collect before recalculating the dynamic limits using the provided textbox, or select a value by pressing the up and down arrows next to the textbox. By default, Quality AnalytiX calculates these limits after every sample (Calculate Everyvalue of1).
-
Enable the All data in batch radio button to use every sample in the most recent group when calculating control limits.
-
Enable the Last N subgroups radio button to use every sample in the most recent set of n subgroups within the most recent group when setting the calculated limits. To specify the number of subgroups to consider when determining the calculated limits, enter a value for N using the provided textbox, or select a value by pressing the up and down arrows next to the textbox. By default, Quality AnalytiX calculates control limits using only the most recent subgroup (N value of 1).
-
Enable the Constantradio button to use a precise set of control limits based on a mean and standard deviation that you define.
-
For theMeanfield, select the ellipsis [...] button to open the
 Select Variable dialog, where you can choose a dynamic data tag to use as the expected mean for the SPC tag's sample values. You can also enter a constant value in the provided textbox.
Select Variable dialog, where you can choose a dynamic data tag to use as the expected mean for the SPC tag's sample values. You can also enter a constant value in the provided textbox.
-
Similarly, for the Sigma field, press the ellipsis [...] button to select a dynamic data tag to use as the expected standard deviation for these values, or enter a constant value in the provided textbox.

Note: The effect that the MeanandSigmavalues have on the control limits within Quality AnalytiX depend on theDistribution Rulesthat you have defined in theProperties tab.
-
-
Continue configuring this SPC tag using the settings on the Properties tab or the Statistics tab.
-
-
If you have enabled the "Constant Limits" radio button within the "Control Limits" tab:
-
Set the UCL (upper control limit), CL (center line), and LCL (lower control limit) for the Primary and Secondary summary values that this SPC tag calculates. You can select the ellipsis [...] button to open the
 Select Variable dialog and choose a dynamic data tag, or you can enter a constant value in the provided textbox.
Select Variable dialog and choose a dynamic data tag, or you can enter a constant value in the provided textbox.
-
|
|
Note: The names of the variables that appear as columns in this section of the tab depend on the Collection Type you choose in the Properties tab. |
-
Continue configuring this SPC tag using the settings on the Properties tab or the Statistics tab.
Statistics Tab
-
The Statistics Tab allows you to configure the number and types of samples to include when Quality AnalytiX calculates summary statistics for this SPC tag, as well as the summary statistics that Quality AnalytiX calculates for the tag.
|
|
Note: If you have left the Collection Typevalue blank, the settings on this tab remain disabled. |
-
In the Specification section of the tab, use the provided drop-down list to prevent Quality AnalytiX from including SPC tag sample values that fall too far outside a set of specification limits. You can set All Limits, Upper Limits only, Lower Limits only, or upper and lower limits with a Default Target.
-
For the Upper Specification Limit field, select the ellipsis [...] button to open the
 Select Variable dialog and choose a dynamic data tag. This data tag specifies the maximum SPC tag value that you want Quality AnalytiX to consider when calculating summary statistics. You can also enter a constant value in the provided textbox.
Select Variable dialog and choose a dynamic data tag. This data tag specifies the maximum SPC tag value that you want Quality AnalytiX to consider when calculating summary statistics. You can also enter a constant value in the provided textbox. -
Repeat the previous step for the Target field to specify a target sample value that this SPC tag should attain.
-
Repeat the previous step for the Lower Specification Limit field to specify the minimum tag value that you want Quality AnalytiX to consider when calculating summary statistics.
|
|
Note:Some of the fields described in these step might be disabled, depending on the types of limits you specified. |
-
In the Statistics Calculation section of the tab, enter a value in the textbox next to the Calculate Every field. This value represents the number of samples that the SPC tag should collect before recalculating summary statistics. You can also select a value by pressing the up and down arrows next to the textbox. By default, Quality AnalytiX calculates these limits after every sample (Calculate Every value of 1).
-
Enable the All Data in Batch radio button to use every sample in the most recent group when calculating summary statistics.
-
Enable the Last N subgroups radio button to use every sample in the most recent set of n subgroups within the most recent group when calculating summary statistics. To specify the number of subgroups to consider when determining these statistics, enter a value for N using the provided textbox, or select a value by pressing the up and down arrows next to the textbox. By default, Quality AnalytiX calculates summary statistics using only the most recent subgroup (N value of 1).
-
In the Process Capability Ratios section of the tab, enable the check box next to each summary statistic you wish to calculate for this SPC tag. The possible summary statistics include:
-
Cp:The process capability, which measures the expected productivity of a processsamplewhose mean lies exactly between its specification limits.
-
Cpu:The process capability for a system sample that has only an upper limit.
-
Cpl:The process capability for a system sample that has only a lower limit.
-
Cpm:Estimate of the process capability index around a specific target value. Also known as the Taguchi capability index.
-
Cpk:Estimate of the process capability index for cases where the distribution of sample values is not centered. It is equal to min(Cpu, Cpl).
-
Cpkm:Estimate of the process capability index around a specific target value for cases where the distribution of sample values is not centered.
-
Cr:The process capability ratio, which estimates the spread of the sample values relative to that of the specification limits. It is equal to 1/Cp.
-
Pp:The process performance, which measures the expected productivity of a processpopulation.
-
Ppu:The process performance for a system population that has only an upper limit.
-
Ppl:The process performance for a system population that has only a lower limit.
-
Ppm:Estimate of the process performance index around a specific target value.
-
Ppk:The process performance for cases involving non-centered distributions. It is equal to min(Ppu, Ppl).
-
Ppkm:The process performance around a specific target value for non-centered distributions.
-
Mean:The expected average of the process values.
-
Sigma:The expected standard deviation of the process values.
-
Avg:The actual average of this SPC tag's sample values.
-
StdDev:The actual standard deviation of this SPC tag's sample values.
-
Skew:Measures the symmetry of the curve generated by graphing this SPC tag's sample values on a plot. Data that is skewed to the right results in a positive Skew value, and data that is skewed to the left results in a negative Skew value.
-
Kurtosis: Measures the relative height of a curve generated by graphing this SPC tag's sample values on a plot. A narrow, sharp curve is leptokurtic and contains a Kurtosis value greater than 3. A wide, flat curve is platykurtic and contains a Kurtosis value less than 3. A perfectly Normal peak has a Kurtosis value of exactly 3.
|
|
Note: For more detailed information about the different summary statistics available in the Process Capability Ratios section of the tab, see the Statistics Reference topic. |
-
Enable the check box next to Data is Normal if this SPC tag's samples follow a Normal (Gaussian) distribution.
-
Continue configuring this SPC tag using the settings on the Properties tab or the Control limits tab.
See Also: