Using the JOIN Keyword
A joined table is a result set that is the product of two or more tables. BI Server supports INNER, LEFT OUTER and RIGHT OUTER joins.
The following query retrieves the quantity of products for each order using an INNER join.
Example:
SELECT OrderID, ProductName, Quantity
FROM Products AS p INNER JOIN OrderDetails AS od
ON p.ProductID = od.ProductID
Tip: The selected columns do not have to be qualified when their name is unique among the joined tables.
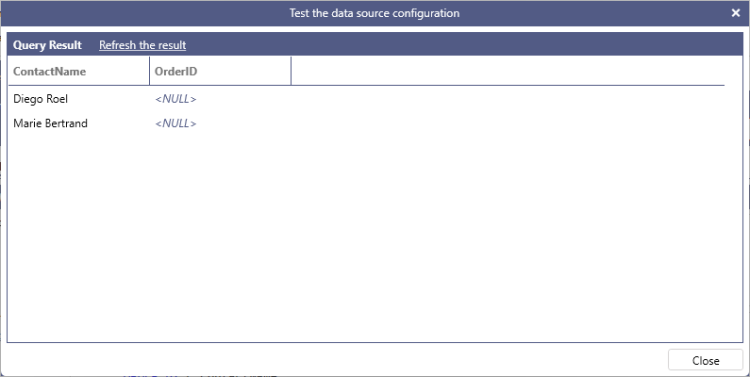
The following example shows a query that uses a LEFT join to display the list of customers without any associated orders.
Example:
SELECT ContactName, OrderID
FROM Customers AS c LEFT JOIN Orders AS o
ON c.CustomerID = o.CustomerID
WHERE o.OrderID IS NULL
ORDER BY c.ContactName
Similarly, the following query uses a RIGHT join to display all order numbers that do not have a customer associated with them.
Example:
SELECT ContactName, OrderID
FROM Customers AS c RIGHT JOIN Orders AS o
ON c.CustomerID = o.CustomerID
WHERE c.ContactName IS NULL
ORDER BY o.OrderID
If relationships between tables are established in the data model, the JOIN keyword can be omitted, however all columns in the query must be fully qualified. BI Server will determine the join path among all the tables that are referenced in the query automatically. The following query calculates the total for each order without explicitly specifying the FROM or JOIN keywords for the Orders and OrderDetails tables.
Example:
SELECT Orders.CustomerID, Orders.OrderDate, SUM(OrderDetails.UnitPrice * OrderDetails.Quantity * (1 - OrderDetails.Discount)) AS OrderTotal
ORDER BY Orders.OrderDate
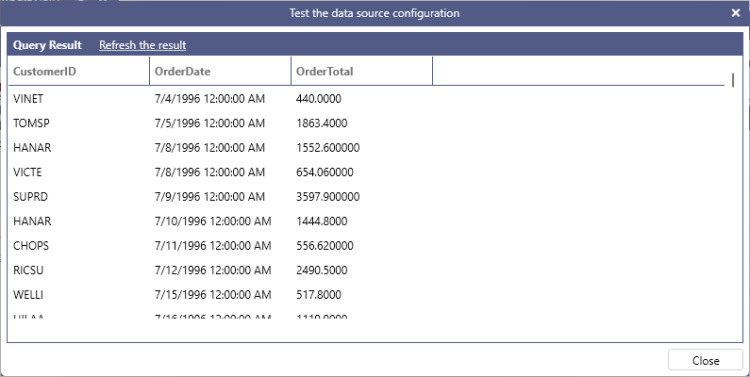
BI Server automatically determines the join path between the Orders and OrderDetails table based on the relationships configured in the model.