Other
Project Commands
There are several commands that can be used to manage a Desktop project in the Workbench. They deal with different types of entities:
- AppProject
- AppServer
- Application
- FileInfo
- SqlServerInfo
An AppProject can contain multiple AppServers. An AppServer can contain multiple Applications.
This is the corresponding hierarchy in the Workbench:
Project Hierarchy in the Workbench

There is no hierarchy for FileInfo and SqlServerInfo.
The commands mimic the following features in the Workbench:
FileInfo and SqlServerInfo actions in the Workbench
To access them, you need to select a Project in the Project Explorer and then go in the Workbench Ribbon and select the two actions "SQL Configuration" and "File Configuration" in the Project Tools section.
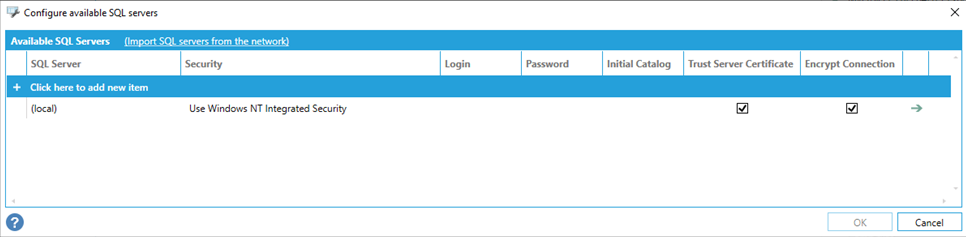
SQL Server Configuration dialog
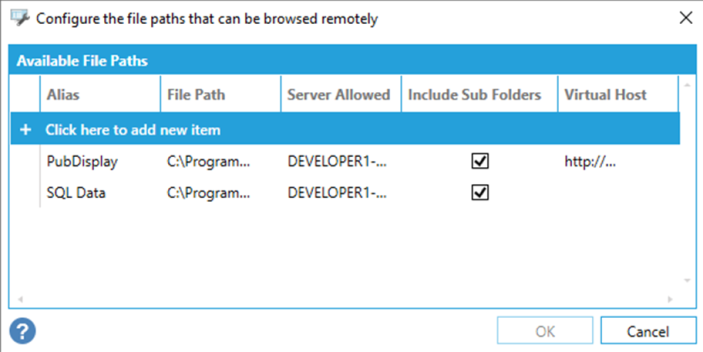
File Info Configuration dialog
The following commands are specific to the ICONICS PowerShell Extension. [See Get-Help for how to get additional information about each individual command.]
|
Command |
Type Name |
Module Name |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbApplication |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbApplications |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbApplicationsByParent |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbAppProject |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbAppProjects |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbAppProjectsRoot |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbAppServer |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbAppServers |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbAppServersByParent |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbFileInfo |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbFileInfoes |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbSqlServerInfo |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbSqlServerInfoes |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
New-WbApplication |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
New-WbAppProject |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
New-WbAppServer |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
New-WbFileInfo |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
New-WbSqlServerInfo |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Set-WbApplication |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Set-WbAppProject |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Set-WbAppServer |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Set-WbFileInfo |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Set-WbSqlServerInfo |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Remove-WbApplication |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Remove-WbAppProject |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Remove-WbAppServer |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Remove-WbFileInfo |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Remove-WbSqlServerInfo |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Task Commands
There are several commands that can be used to manage Workbench tasks. It is possible to get the complete list of the tasks being executed.
Get-WbTasks
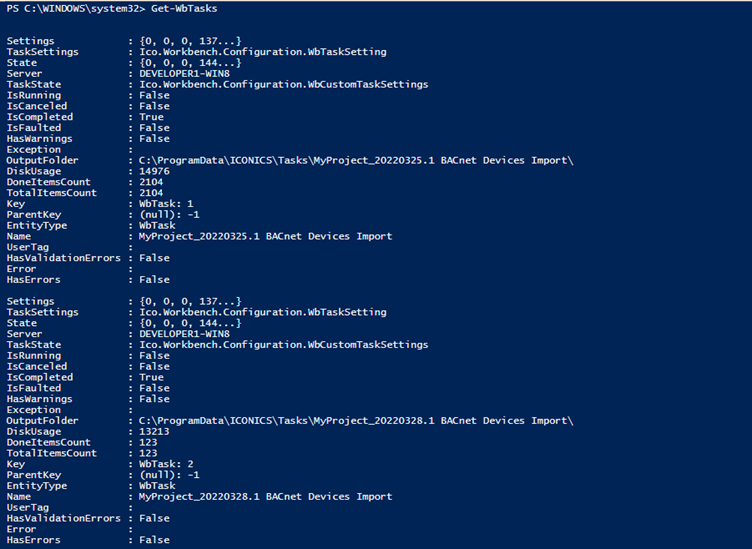
You can get a specific task by its name, key, identifier or by the task itself.
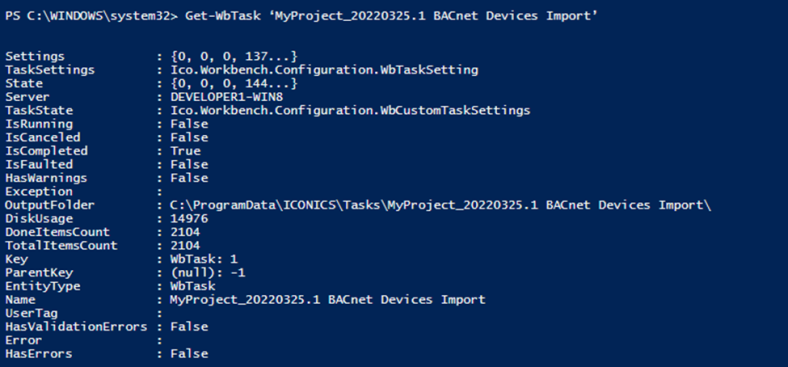
Get-WbTask ‘MyProject_20220325.1 BACnet Devices Import’
Get-WbTask (New-WbKey -Id 1 -TypeName WbTask)
Get-WbTask 1
Get-WbTask (Get-WbTask 1)
You can delete a set of tasks passing and array of keys:
Remove-WbTasks -Keys @((New-WbKey -Id 1 -TypeName WbTask), (New-WbKey -Id 2 -TypeName WbTask))

It is possible to cancel a running task specifying it by name, key, identifier or task itself:
Set-WbCancelTask ‘MyProject_20220325.1 BACnet Devices Import’
Set-WbCancelTask (New-WbKey -Id 1 -TypeName WbTask)
Set-WbCancelTask 1
Set-WbCancelTask (Get-WbTask 1)


Consider that the task must be running, otherwise an error will occur again.
If the task generated a file (pack file or export file), there exist some commands to download them. You need to specify the task and the target path.
Get-WbExportFile -Task [task] -TargetPath [target_path]

Get-WbPackFile -Task [task] -TargetPath [target_path]

The following commands are specific to the ICONICS PowerShell Extension. [See Get-Help for how to get additional information about each individual command.]
|
Command |
Type Name |
Module Name |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbTask |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbTasks |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Remove-WbTasks |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Set-WbCancelTask |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbPackFile |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
|
Cmdlet |
Get-WbExportFile |
IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Audit Log Commands
There are several commands that can be used to manage Audit Log Messages.
It’s possible to enable/disable the Audit Log:
Set-WbEnableAuditLog -IsEnabled 1 (to enable it)Set-WbEnableAuditLog -IsEnabled 0 (to disable it)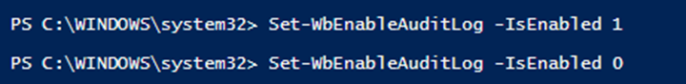
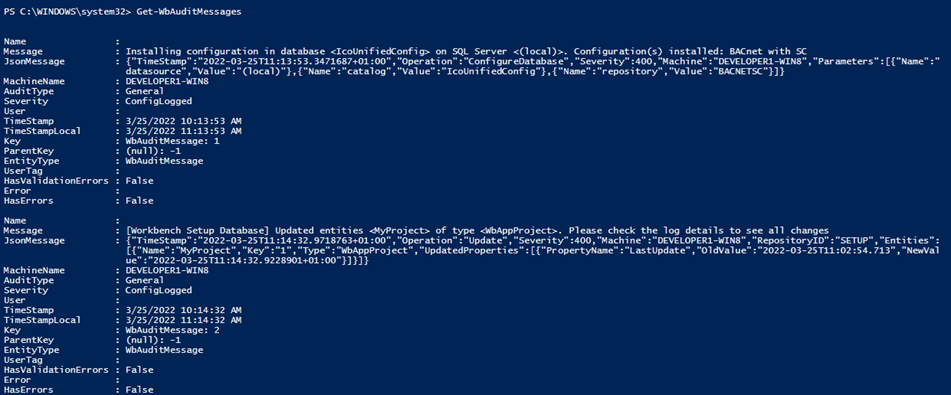
You can get all the messages in the Audit Log or a specific one (using id, key or entity itself).
Get-WbAuditMessages
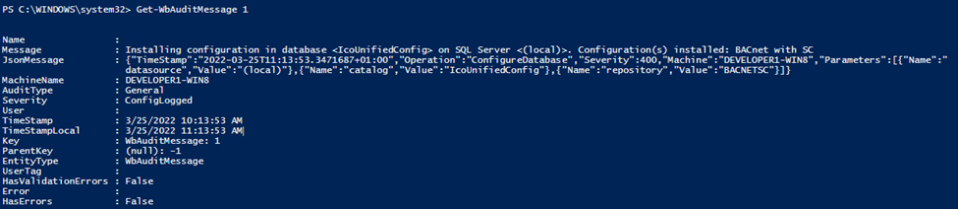
Get-WbAuditMessage 1
Get-WbAuditMessage (New-WbKey -Id 1 -TypeName WbAuditMessage)
Get-WbAuditMessage (Get-WbAuditMessage 1)
The following commands are specific to the ICONICS PowerShell Extension. [See Get-Help for how to get additional information about each individual command.]
Command | Type Name | Module Name |
Cmdlet | Get-WbAuditMessage | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | Get-WbAuditMessages | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | Set-WbEnableAuditLog | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Databases Commands
There are several commands that can be used to manage Databases. It is possible to attack/detach databases:
Set-WbDetachRemoveDatabase
The parameters are:
SqlServerKey: the key of the SqlServerInfo (the instance of SQL Server where the database is)
DatabaseName: the name of the database to be detached/removed
ShouldDetach: 1 if the database should be detached

Set-WbAttachDatabase
The parameters are:
SqlServerKey: the key of the SqlServerInfo (the instance of SQL Server where the database is)
DatabaseName: the name of the database to be attached
FileToAttach: the absolute path to the file (.MDF) to be attached

It is possible to backup/restore databases:
Set-WbBackupDatabaseThe parameters are:
SqlServerKey: the key of the SqlServerInfo (the instance of SQL Server where the database is)
DatabaseName: the name of the database to be backed up
BackupName: the name of the backup file
BackupDescription: the description of the backup operation

To get the collection of restore points of a database you can execute this command:
Get-WbRestorePoints
The parameters are:
SqlServerKey: the key of the SqlServerInfo (the instance of SQL Server where the database is)
DatabaseName: the name of the database

Then you can restore a database using the path of a restore point:
Set-WbRestoreDatabase
The parameters are:
SqlServerKey: the key of the SqlServerInfo (the instance of SQL Server where the database is)
DatabaseName: the name of the database to be restored
BackupName: the path of the restore point to be restored

The following commands are specific to the ICONICS PowerShell Extension. [See Get-Help for how to get additional information about each individual command.]
Command | Type Name | Module Name |
Cmdlet | Get-WbRestorePoints | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | Set-WbAttachDatabase | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | Set-WbBackupDatabase | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | Set-WbDetachRemoveDatabase | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | Set-WbRestoreDatabase | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Keys Commands
There are several commands that can be used to manage Keys.
A key is a reference to an existing entity, and it consists of:
Id: an integer that identifies the entity in the configuration database
TypeName: a string representing the name of the type of the entity
With a key, you can uniquely identify an entity.
We have commands that can be used to:
create an empty key,
create a root key,
create a type,
create a key.
Here are some examples:


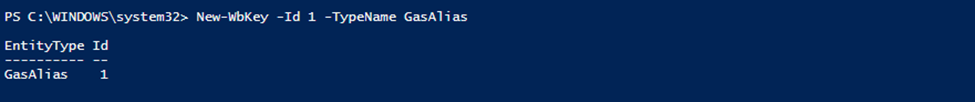

The following commands are specific to the ICONICS PowerShell Extension. [See Get-Help for how to get additional information about each individual command.]
Command | Type Name | Module Name |
Cmdlet | New-WbEmptyKey | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | New-WbKey | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | New-WbRootKey | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | New-WbType | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Encryption Commands
We have command to encrypt/decrypt string values. To encrypt a value we can use:
Set-WbEncryption ‘valueToBeEncrypted’The command returns a byte array with the value encrypted using ICONICS library IcoSecurityCryptography calling the SaltAndHash method.
To verify if an encrypted value is valid we can use:
Set-WbDecryption -Value [decryptedValueToBeTested] -Hash [encryptedValueToBeTested]The command returns true if the encrypted value when decrypted is equal to the expected decrypted value.
Here some examples:


The following commands are specific to the ICONICS PowerShell Extension. [See Get-Help for how to get additional information about each individual command.]
Command | Type Name | Module Name |
Cmdlet | Set-WbDecryption | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | Set-WbEncryption | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Find/Copy/Paste/Multiply Commands
There are several commands that can be used to mimic Find/Copy/Paste/Multiply features available in Workbench.
To copy/paste or move/paste an entity you can use:
Set-WbCopyPasteThe parameters are:
Provider: the provider where we are copying/moving the entities
SourceKeys: an array of the keys of the entities to be copied/moved
TargetParentKey: the key of the target parent entity
PasteType: the type of paste operation (Move or Copy)
For example, here we are copying the GasAlias ‘Building’ in the ‘GasAliases’ root folder:
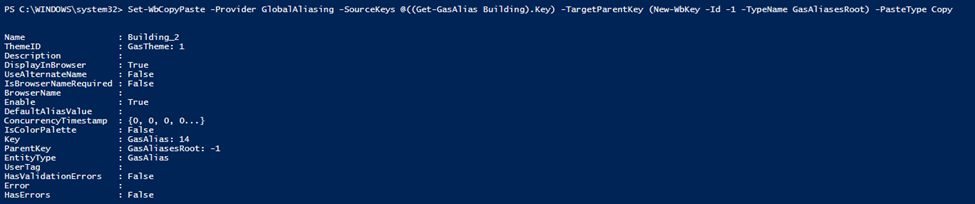
To find/replace an entity you can use:
Set-WbFind
The parameters are:
Provider: the name of the provider
FindWhat: what text to search for
ParentKey: The root of the tree branch where the search starts. If NULL text will be searched in the whole database.
FindOn: an array of FindOn entities. They are composed by EntityType/PropertyName and they specify the properties we will match during the find operation
RequestedPropertyNames: a list of properties that must be returned by the server in order to optimize the output. Null means all properties.
The result of the call is a collection of FindResult. A find result contains the parent path, the entity and the blob version of the entity, for each found entity.
For example here, we can find the GasAlias entities with ‘Building’ contained in their name under the GasAliases root folder:

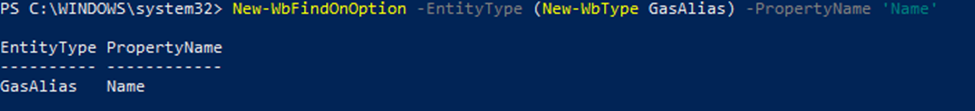
To create a FindOn entity you can call:
New-WbFindOnOption
The parameters are:
EntityType: the type of the entity (you can use New-WbType to create it)
PropertyName: a string representing the name of the property
Here, for example, we are creating a FindOnOption to look for the property ‘Name’ in the GasAlias entities:
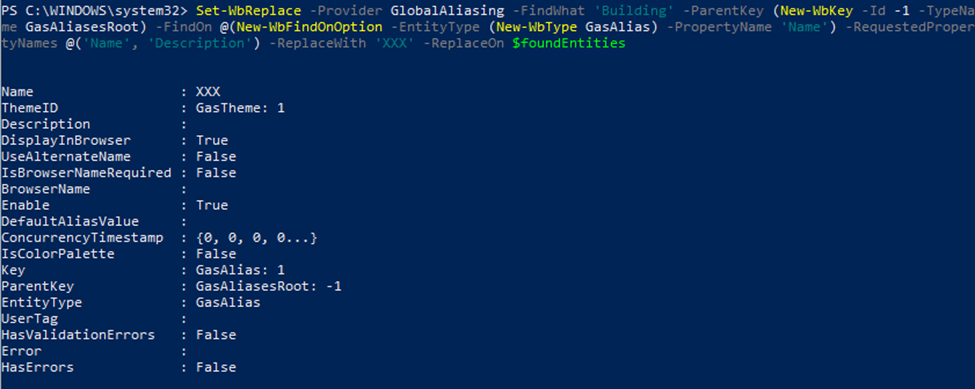
To have a complete find/replace you can use:
Set-WbReplace
The parameters are:
Provider: the provider where we are finding the entities
FindWhat: the text to search for
ParentKey: The root of the tree branch where the search starts. If NULL text will be searched in the whole database.
FindOn: an array of FindOn entities. They are composed by EntityType/PropertyName and they specify the properties we will match during the find operation
RequestedPropertyNames: A list of properties that must be returned by the server in order to optimize the output. Null means all properties.
ReplaceWith: the text that should replace the found text
ReplaceOn: If specified, it replaces the ‘ParentKey’ parameter. But ‘FindOn’ parameter is still applied.
Here an example on how to replace all the GasAliases with name containing the text ‘Building’ with ‘XXX’:

If you want to remove a collection of entities recursively, you can execute:
Remove-Recursive
The parameters are:
Provider: the provider where we want to delete recursively
Keys: an array of the keys of the entities we want to delete recursively
Here and example:

The following commands are specific to the ICONICS PowerShell Extension. [See Get-Help for how to get additional information about each individual command.]
Command | Type Name | Module Name |
Cmdlet | Set-WbCopyPaste | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | Set-WbFind | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | Set-WbReplace | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Cmdlet | Remove-WbRecursive | IcoWorkbenchPowershell |
Security Commands
We have some commands to login/logout into ICONICS Security.
To Login we can execute:
Set-WbUserLogin
Set-WbUserLoginAsync
With the first command the login will be done synchronously, while with the other command it will be done asynchronously.
In both the case the user can pass the parameters or not. With no parameters you’ll be prompted to enter your credentials:
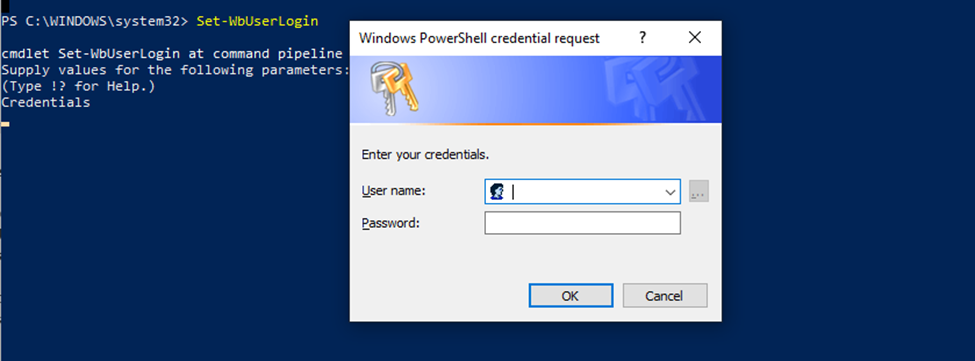
Otherwise you can explicitly pass the credentials as parameters:

To logout we can execute
Set-WbUserLogout
With the first command the logout will be done synchronously, while with the other command it will be done asynchronously.
Import/Export Commands
There are several commands to execute import/export operations.
To export a configuration you can execute:
Export-WbConfiguration
The parameters are:
Root: it is the EntityUniqueKey associated to the Entity from where you want to export the data. To create a key you can use New-WbRootKey (for the root) or New-WbKey with the Id and the type of the entity.
GenerateRelativePaths: if you want to generate the export file with relative paths or not
Format: csv/xml/excel
Delimiter: the char you want to use to delimit the data in case of csv file
ChildrenOnly: if you want to export only the children of the root or also the root
Provider: the provider you want to export
If we want to export the whole HH configuration:

If you call the command, it runs a task on the server. Then you can get information about the status of the task:
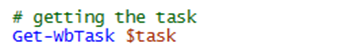
If it is completed, you can call the command to download the export file.

If you want to export just the data under DataCollections\Conditional Logging, you only need to change the key:

and call again the export.
To import into a configuration you can execute
Import-WbConfiguration
The parameters are:
Root: it’s the EntityUniqueKey associate to the Entity from where you want to import the data. To create a key you can use New-WbRootKey (for the root) or New-WbKey with the Id and the type of the entity.
Path: the path where the file to be imported is
Format: the format (csv/xml/excel) of the file to be imported
Delimiter: the char used as delimiter for csv files
ImportMode: Create/Update/Create and Update/Delete
ShouldBackup: true, if we want to backup the database before importing
PurgeDatabase: true, if we want to delete the database before importing
AllowPartialImport: true, if we want the import to continue in case of errors
Provider: the provider where we are importing
This is how it looks if we import on the whole HH configuration:

If you call the command, it uploads the file to the server and it runs a task. Also in this case you can see the status of the task saying:

Pack & Go Commands
There are several commands to execute Pack/Unpack/Explore operations.
To pack a configuration you can execute
Set-PackWbConfiguration
The parameters are:
ProjectKey: the EntityUniqueKey that identifies the project you want to pack
UserComments:user comments to be added to the package
EnableFindReplace: to enable the find replace feature
FindReplaceItems:the collection of items of the find/replace
CompressFiles:specifies if we want to compress the files
ProtectionLevel:the protection level of the package (None, Encrypted, Protected)
Password:the password to be used in case of encrypted/protected packages
Files:the collection of files to be added to the package
GwxPackUserSettings: specifies if we want to pack GraphWorX user settings
GwxPackWindowsLayout: specifies if we want to pack GraphWorX windows layout settings
GwxResolveDependencies: specifies it we have to resolve GraphWorX dependencies
PackItems: the collection of items to be packed
To fill in an easier way the parameters (the collections), we have some helper methods:
New-PackAndGoFindReplaceSettings/Set-PackAndGoFindReplaceSettings to create/update a find replace item
The parameters to be set in this case are:
OriginalValue: the original string to be replaced
Alias: the string alias
You can also specify the granularity of the find/replace item with All, Text, DataSource…. parameters
New-PackAndGoFileSettings/Update-PackAndGoFileSettings to create/update file items
The parameter to be set is just the -FileName
New-PackItemSettings/Set-PackItemSettings to create/update a pack item
The parameters are:
HostName: the server where the configuration is
Provider: the provider you want to pack
Key: the entity unique key of the root entity of the pack item
For example, if we want to pack HH under DataCollections\ConditionalLogging and all AssetCatalog and a few files. If we also want to replace the string ‘localhost’ with the alias [HOST], and ‘GEN’ with [PREFIX], we can start creating the find/replace settings:

The we can create the files settings
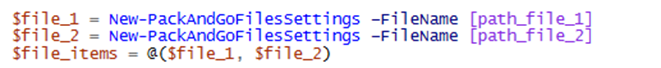
And then the pack items
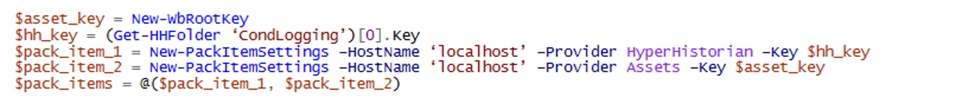
Now the pack operation is called:

Once you call the command, it starts a task on the server.
In this case, you can also see the status of the task saying:

If the task is completed you can download the package:
Get-WbPackFile –Task $task –TargetPath [your_target_path]
To unpack into a configuration you can execute
Set-UnpackWbConfiguration
The parameters are:
ProjectKey: the EntityUniqueKey that identify the project where you want to unpack
Path: the path of the package we want to unpack
Password: the password needed to open a protected/encrypted package
EnableFindReplace: to enable the find replace feature
ImportMode: Create/Update/Create and Update/Delete
DeleteNonExistentItems: True, if we want to delete non existent items
FindReplaceItems: the collection of items of the find/replace
GwxPackSettings: specifies if we want to pack GraphWorX user settings
GwxPackWindowsLayout: specifies if we want to pack GraphWorX windows layout settings
Files: the collection of files to be added to the package
UnpackItems: the collection of items to be unpacked
In this case we can still use New-PackAndGoFindReplaceSettings/Set-PackAndGoFindReplaceSettings to create/update a find replace item
But the parameters needed are:
Alias: the alias to be replaced
NewValue: the new value that replaces the Alias
To create the unpack items we can use New-UnpackItemSettings/Set-UnpackItemSettings.
The parameters are:
HostName: the name of the server where we want to unpack
Provider: the provider
OriginalHostName: the name of the server where we packed the item we want to unpack
Key: the target entity unique key
DataSourceName: the name of the datasource where we want to unpack
DataBaseName: the name of the database where we want to unpack
SecurityMode/Username/Password: credentials to access to the database
Now we can upack the previous package in the project:
We can start creating the find/replace settings:

In this case, if the parameter is not passed, we used the value in the settings of the package, otherwise we merge the parameter with them.
Then we can continue with the files items: we only accept files coming from the parameters that also exist in the package. We just update the location of the file.

Then we continue with the unpack items:
In this case, we also accept only the items coming from the parameters that also exist in the package. Then we only update them.

Now we are ready to call the command:

Once you call the command, it uploads the package on the server, and then it starts the unpack operation.
In this case, we can also see the status of the task saying:

You can manage the protection level of a package using Get-PackProtectionLevel and Set-PackProtectionLevel commands.
Get-PackProtectionLevel needs just the file path of the package and returns the protection level
Set-PackProtectionLevel needs:
FileName: the path of the package
ProtectionLevel: the new protection level
Password: the password to access the package if it’s already protected/encrypted
NewPassword: the new password
TargetPath: the path where we want to save the new package
For example, we want to enable password protection:

Then we want to enable the encryption:

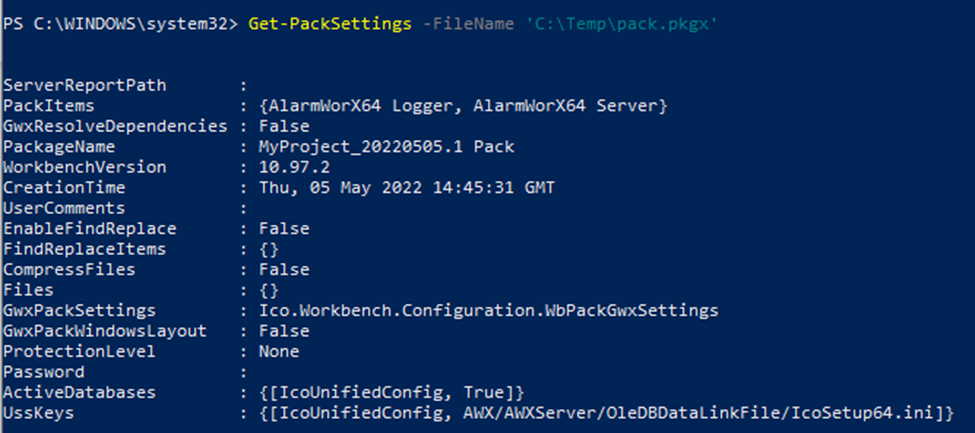
You can get all the settings of a package (something similar to a package explore) using the commandGet-PackSettings.
You just need to specify the path of the file and eventually the password if the package is protected/encrypted.
See Also: